Health Tips about Cardiovascular Diseases
Positive Communication in the Workplace – Praise and Appreciation


Department of Health
The Population Health Survey 2020-22, which adopted the Framingham Risk Model to predict the risk of cardiovascular outcomes including coronary heart diseases, strokes, peripheral artery diseases and heart failure among local adult population, found that 14.5% of persons aged 30–74 had higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases (i.e. ≥20% in the next decade).
To lower the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, we are advised to note the following:

 Consuming a healthy diet helps prevent malnutrition in all its forms, including overweight and obesity. We are encouraged to eat according to the “Healthy Eating Food Pyramid”. Apart from limiting the consumption of fat, salt and sugars, adults should eat at least five servings of fruit and vegetables per day, choose whole grains over refined grains and reduce the consumption of processed meat. For more details about healthy eating, please refer to the pamphlet at www.chp.gov.hk/files/her/exn_nutp_025b_en.pdf.
Consuming a healthy diet helps prevent malnutrition in all its forms, including overweight and obesity. We are encouraged to eat according to the “Healthy Eating Food Pyramid”. Apart from limiting the consumption of fat, salt and sugars, adults should eat at least five servings of fruit and vegetables per day, choose whole grains over refined grains and reduce the consumption of processed meat. For more details about healthy eating, please refer to the pamphlet at www.chp.gov.hk/files/her/exn_nutp_025b_en.pdf.

 We should make physical activity a “must do” habit. For optimal health, adults are advised to do at least 150–300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity (such as brisk walking); or at least 75–150 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity (such as jogging); or an equivalent amount of physical activity throughout the week. We should also reduce sedentary time and replace sitting with physical activity of any intensity including light-intensity physical activity (such as light walking). For more information about “10,000 Steps a Day”, please visit the Change for Health website: www.change4health.gov.hk/en/physical_activity/10000_steps_a_day
We should make physical activity a “must do” habit. For optimal health, adults are advised to do at least 150–300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity (such as brisk walking); or at least 75–150 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity (such as jogging); or an equivalent amount of physical activity throughout the week. We should also reduce sedentary time and replace sitting with physical activity of any intensity including light-intensity physical activity (such as light walking). For more information about “10,000 Steps a Day”, please visit the Change for Health website: www.change4health.gov.hk/en/physical_activity/10000_steps_a_day
/index2.html.

 Smoking can permanently damage the heart and blood vessels, leading to cardiovascular diseases. For the sake of health, non-smokers should never start smoking while smokers should quit immediately. For free quit tools and services, please visit the designated website: www.livetobaccofree.hk or call the Quitline 1833 183.
Smoking can permanently damage the heart and blood vessels, leading to cardiovascular diseases. For the sake of health, non-smokers should never start smoking while smokers should quit immediately. For free quit tools and services, please visit the designated website: www.livetobaccofree.hk or call the Quitline 1833 183.
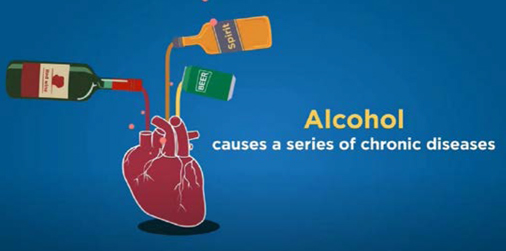
 Alcohol consumption is associated with the risks of developing non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, liver diseases, certain cancers and alcohol use disorders. While individuals without a habit of drinking alcohol should not start drinking, current drinkers should appraise their drinking habits, realise the potential harms associated with drinking and appreciate the benefits of stopping alcohol consumption. To access useful toolkits including the electronic alcohol screening and brief intervention tool (e-SBI), a self-help booklet for drinkers and other health educational materials pertaining to alcohol and health, please visit the Change for Health website www.change4health.gov.hk/tc/alcohol_aware/index.html.
Alcohol consumption is associated with the risks of developing non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, liver diseases, certain cancers and alcohol use disorders. While individuals without a habit of drinking alcohol should not start drinking, current drinkers should appraise their drinking habits, realise the potential harms associated with drinking and appreciate the benefits of stopping alcohol consumption. To access useful toolkits including the electronic alcohol screening and brief intervention tool (e-SBI), a self-help booklet for drinkers and other health educational materials pertaining to alcohol and health, please visit the Change for Health website www.change4health.gov.hk/tc/alcohol_aware/index.html.
Persons aged 18 or above are recommended to have their blood pressure checked at least once every two years; persons aged 45 or above are recommended to undergo screening for type 2 diabetes at a minimum of three-year intervals; and persons aged 50–70 are recommended to undergo screening for hyperlipidaemia once every three years. More frequent testing is recommended when risk factors of cardiovascular diseases (such as overweight and obesity) are present. We may consult doctors about the need for screenings for hypertension, type 2 diabetes and hyperlipidaemia.